The results obtained in the CIGAT Biofactory Joint Unit have boosted the development of new R&D&I solutions in the Ourense biofactory, through the new ECOVAL and WalNUT projects.
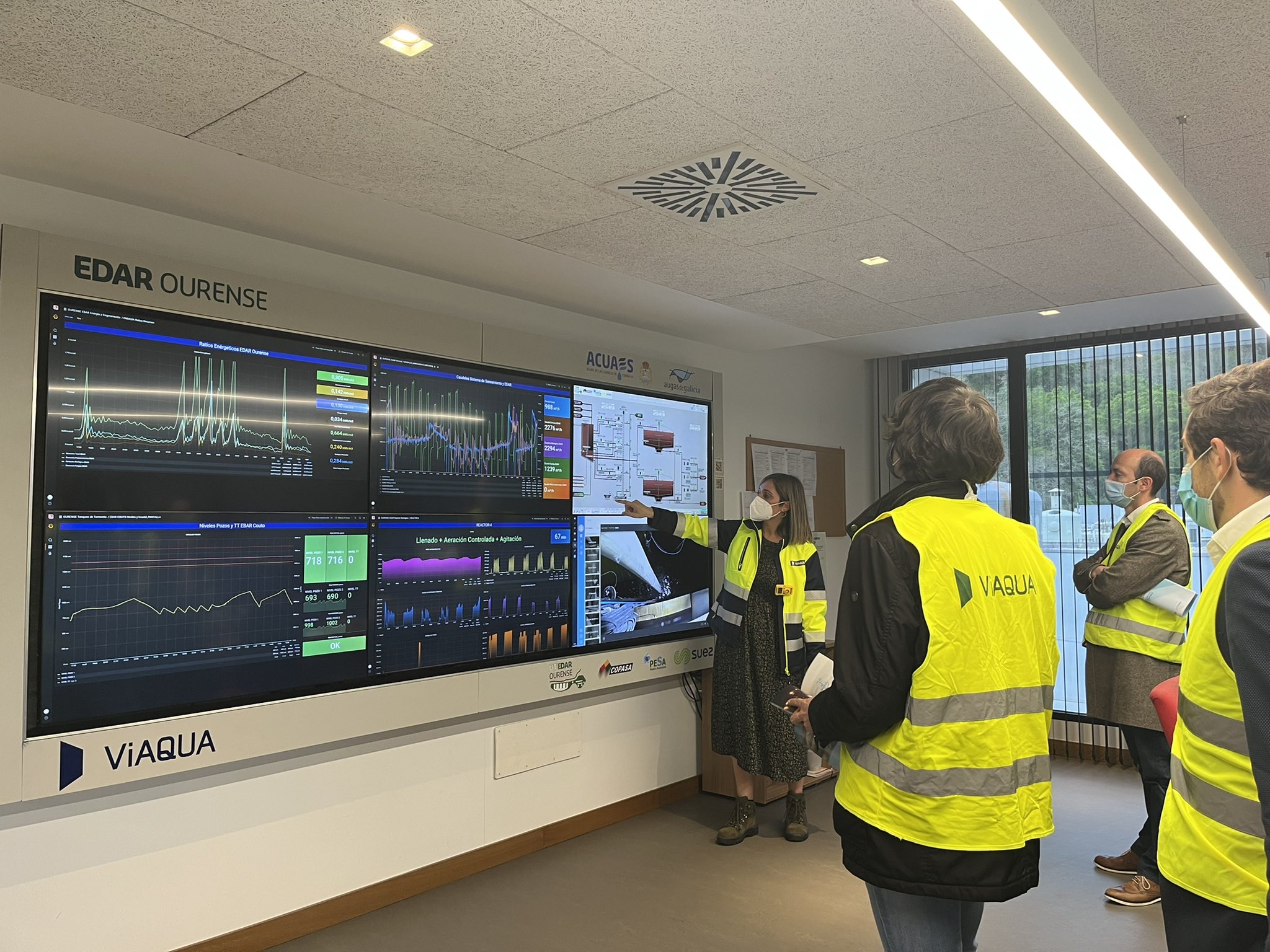
The Ourense Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) is currently a benchmark in circular economy thanks to the transformation it has undergone in recent years by becoming a biofactory, i.e. a new model of facility based on the principles of circular economy, where water is regenerated for subsequent reuse, renewable energy is produced and waste is transformed into resources. In this way, the value of resources is maximised by promoting an energy-neutral model that contributes to zero waste.
The success of the results obtained in the CIGAT Biofactory Joint Unit, the result of the public-private collaboration between Viaqua, Cetaqua and the Galician Innovation Agency (GAIN), has served as a basis for the development and implementation of new R&D&I projects, this time with a focus on Europe, such as H2020 Walnut and Interreg Sudoe ECOVAL.
Both projects, aligned with the 2030 Agenda, position Galicia as a European benchmark in terms of the implementation of innovative technologies developed for the efficient management of urban flows and the consequent use of waste for a lower environmental impact.
ECOVAL (Coordination strategies for the management and recovery of sludge and organic waste in the SUDOE region), headed by Cetaqua Galicia, is based on the valorisation of urban organic waste and sewage sludge to obtain bio-products such as Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA), useful for the plastics, lubricants and paint industries, among others. Walnut, led by CARTIF, seeks the recovery of nutrients and the subsequent production of biofertilisers, thus preventing the contamination of water bodies and promoting circularity in the fertiliser industry within the framework of the European Union.

More than 100 people attended the event “From wastewater treatment plants to biofactories: the potential of water in the circular economy”, to learn about the technical advances and results of the two European projects being developed in Ourense.
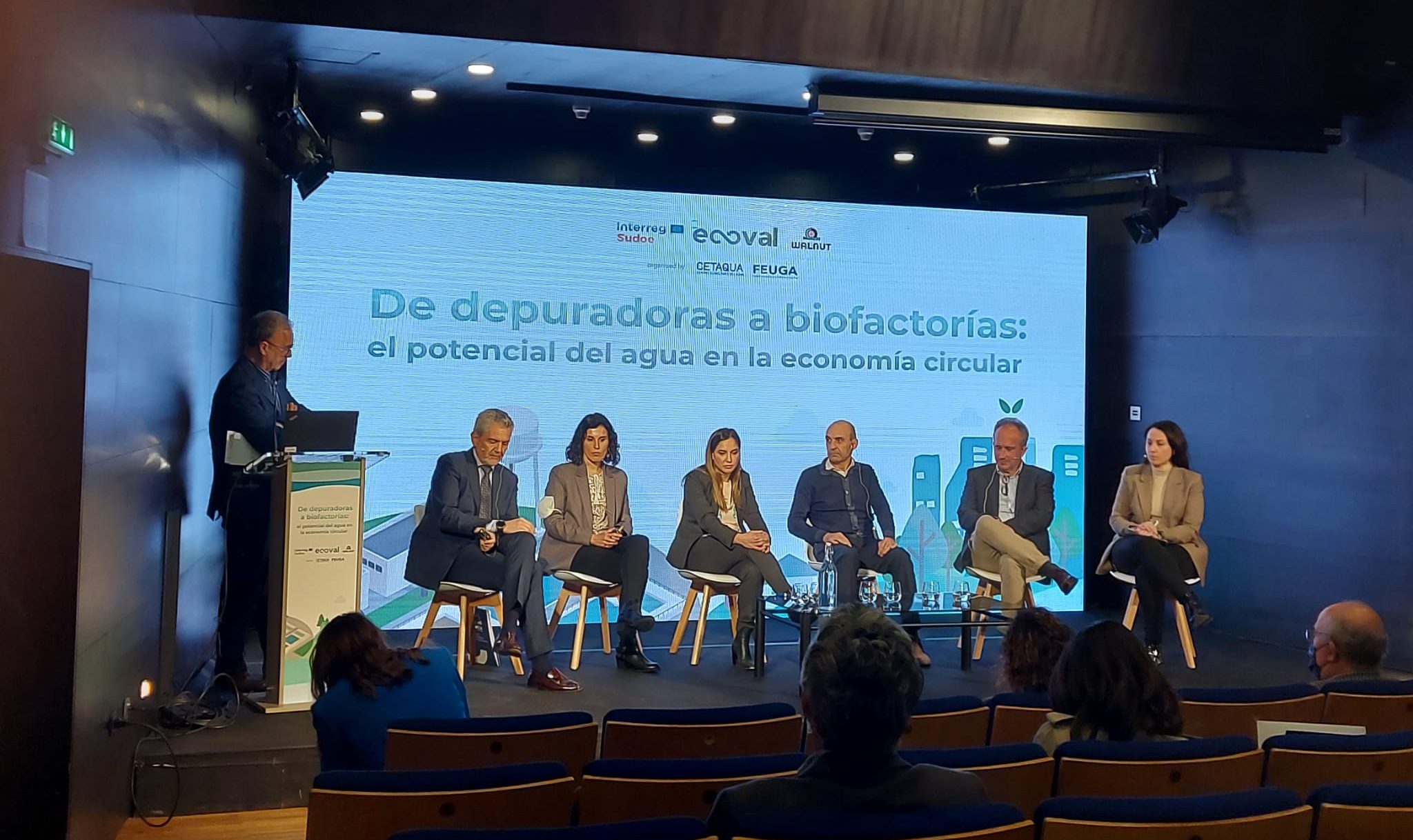
During the event “From wastewater treatment plants to biofactories: the potential of water in the circular economy”, held this morning in the auditorium of Ourense, leading representatives of public administration, universities and companies have come to discuss about the existing social, legal and market barriers for the valorisation of high added value products present in wastewater, useful for industry and agriculture.
The Deputy Mayor of Ourense, Armando Ojea, opened the event by highlighting “the development of research projects in Ourense, which allow giving a second chance to WWTP waste, making the city more sustainable”.
Actors from the entities involved, such as Agbar, Cetaqua and the CARTIF Technology Centre, have intervened to talk about the circular economy models implemented, the valorisation of matter in fatty acids and nutrients applied in the fertiliser industry carried out. On the other hand, the University of Vigo and FEUGA, have participated focusing on the legislative and transfer barriers for the transformation of wastewater treatment plants into biofactories.
The end users of the extracted resources, represented by Repsol, Fertiberia and Grupo Valora have highlighted during their interventions the viability of the application of these compounds in the chemical, petrochemical and fertiliser industries as a key step to promote circular and sustainable models.
During the round table moderated by the Professor of Chemical Engineering at the University of Santiago de Compostela (USC), Juan Manuel Lema, representatives of the Diputación de Ourense, Cetaqua, Viaqua, Repsol, Fundación Patrimonio Natural de Castilla y León (FPNCyL) and Fertiberia met to discuss the potential of water within the circular economy.
Juan José Vázquez, head of Water of the Xunta de Galicia in Ourense, has been in charge of closing the event highlighting the importance of projects like these to build a sustainable future and deal with the problem of the lack of resources and the increase of waste.
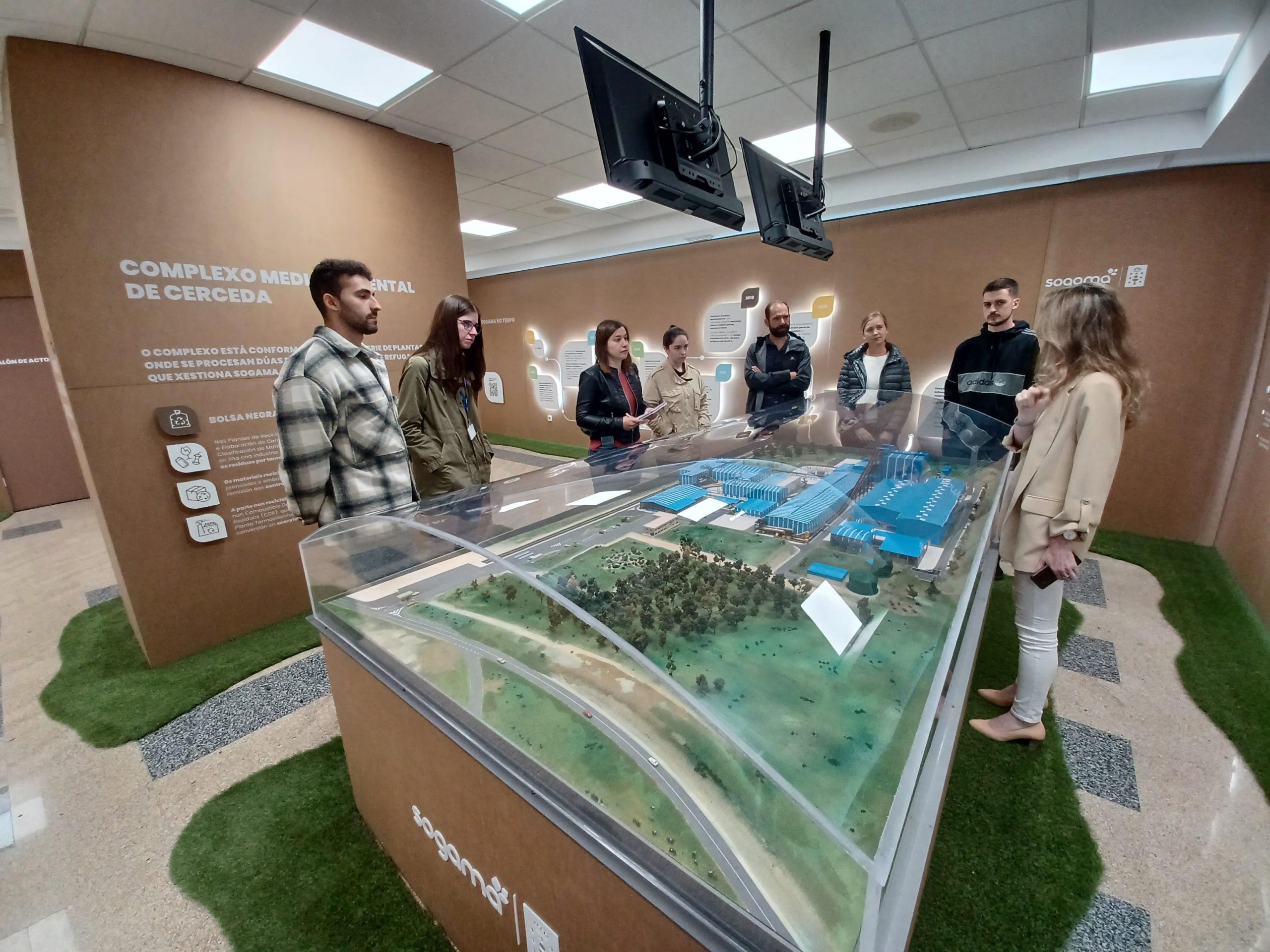
The day ended with a guided tour of the Ourense biofactory, where attendees had the opportunity to see, first hand, the facilities and technologies applied for both projects.